Introduction: The Role of AI in Conflict Resolution
The Evolving Landscape of Conflict Resolution
Conflict is an inherent part of human interaction, whether in personal relationships, business negotiations, or international diplomacy. Traditionally, conflict resolution has relied on human mediators—individuals skilled in facilitating communication, understanding perspectives, and guiding parties toward mutually acceptable solutions. However, the digital age has introduced new complexities and scales of conflict, necessitating innovative approaches. This is where Artificial Intelligence (AI) steps in, offering a transformative role in how we understand and resolve conflicts.
The Rise of AI in Mediation
AI’s ability to process vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and provide unbiased insights makes it a powerful tool in conflict resolution. AI agents can analyze communication patterns, detect emotional cues, and predict potential outcomes, all while remaining neutral and objective. This introduction explores the burgeoning role of AI in conflict resolution, examining how it is reshaping traditional methods and opening new avenues for resolving disputes.
Why AI? The Key Advantages
The integration of AI into conflict resolution brings several key advantages:
Efficiency: AI can process information and generate potential solutions much faster than human mediators.
Objectivity: AI algorithms are designed to be unbiased, ensuring fair and impartial analysis.
Scalability: AI can handle multiple conflicts simultaneously, making it suitable for large-scale applications.
Accessibility: AI-powered mediation can be available 24/7, providing timely assistance regardless of geographical constraints.
The Promise of AI Mediation
As AI technology advances, its potential in conflict resolution continues to grow. From online dispute resolution platforms to internal corporate mediation systems, AI agents are being deployed to facilitate communication, identify common ground, and guide parties toward resolution. This article delves into the core concepts, technologies, and ethical considerations surrounding AI as a digital mediator, exploring its current applications and future possibilities.
Understanding Conflict Dynamics: Human vs. Machine Perspectives
Conflict is a complex and multifaceted phenomenon rooted in human emotions, perceptions, and social interactions. To appreciate how AI agents can act as digital mediators, it is essential to understand the fundamental dynamics of conflict from both human and machine perspectives.
From the human side, conflicts often arise due to misunderstandings, differing values, interests, or goals, and emotional responses such as anger, fear, or frustration. Humans rely heavily on empathy, intuition, and contextual knowledge to navigate these emotional and social nuances during mediation. The ability to read body language, tone of voice, and unspoken cues plays a crucial role in resolving disputes effectively.
In contrast, AI agents approach conflict through data-driven analysis. They process large volumes of textual or verbal communication, identify patterns, and detect sentiment using natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning algorithms. While AI lacks genuine empathy or emotional experience, it compensates by offering consistent, unbiased assessments and the ability to analyze conflicts at scale.
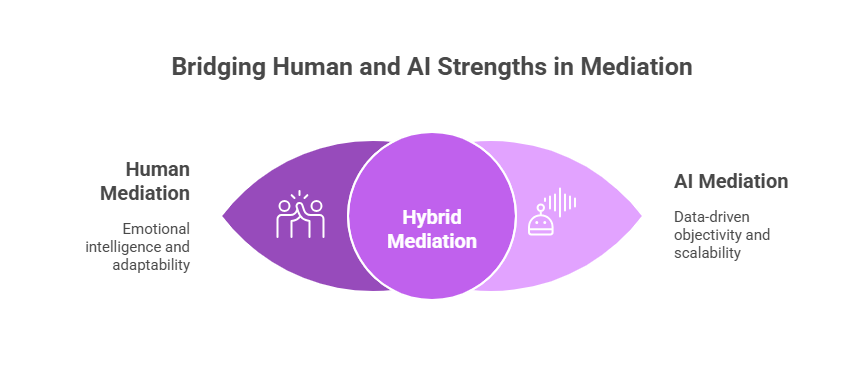
Understanding these differing perspectives highlights both the strengths and limitations of AI in mediation. Human mediators excel in emotional intelligence and adaptability, while AI agents bring speed, objectivity, and scalability. The most effective conflict resolution strategies often combine these strengths, leveraging AI to support human mediators or to handle routine disputes autonomously.
What Is a Digital Mediator? Defining AI Agents in Mediation
A digital mediator is an AI-powered system designed to facilitate conflict resolution by acting as an impartial intermediary between disputing parties. Unlike traditional human mediators, digital mediators leverage advanced algorithms, natural language processing, and machine learning to analyze communication, identify points of contention, and suggest pathways toward agreement.
AI agents in mediation are programmed to understand the context of disputes, interpret the emotions and intentions behind messages, and generate recommendations that aim to satisfy the interests of all parties involved. These agents can operate in various formats, such as chatbots, virtual assistants, or integrated platforms within communication tools.
The core functions of a digital mediator include detecting conflict triggers, managing dialogue flow, proposing compromises, and monitoring the progress of negotiations. By automating these tasks, AI agents can reduce the time and cost associated with traditional mediation while maintaining neutrality and consistency.
Digital mediators are increasingly used in areas like customer service disputes, workplace conflicts, online marketplaces, and even legal negotiations. Their ability to handle multiple cases simultaneously and provide 24/7 availability makes them a valuable complement to human mediators, especially in environments where rapid or large-scale conflict resolution is needed.
Core Technologies Behind AI Mediation Agents
AI mediation agents rely on a combination of advanced technologies that enable them to understand, analyze, and facilitate conflict resolution effectively. The key technologies include natural language processing (NLP), machine learning (ML), sentiment analysis, and knowledge representation.
Natural Language Processing allows AI agents to comprehend and interpret human language in text or speech form. This capability is crucial for understanding the content and context of communications between conflicting parties. NLP techniques help the agent parse sentences, recognize intent, and extract relevant information from conversations.
Machine Learning enables AI agents to improve their performance over time by learning from past mediation cases and user interactions. Through supervised or reinforcement learning, these agents can identify successful negotiation strategies, predict outcomes, and adapt their responses to different conflict scenarios.
Sentiment Analysis is used to detect emotions and attitudes expressed in communication. By analyzing tone, word choice, and phrasing, AI agents can gauge the emotional state of participants, which is vital for tailoring mediation approaches and de-escalating tensions.
Knowledge Representation involves structuring information about conflict resolution principles, negotiation tactics, and domain-specific rules. This allows AI agents to apply logical reasoning and generate meaningful suggestions that align with best practices and legal or organizational frameworks.
Together, these technologies empower AI mediation agents to act as effective digital mediators, combining linguistic understanding, emotional insight, and strategic reasoning to facilitate constructive dialogue and resolution.
Applications of AI in Conflict Resolution: Real-World Examples
AI is increasingly being applied in various conflict resolution scenarios, demonstrating its versatility and potential to transform how disputes are managed. Here are some real-world examples:
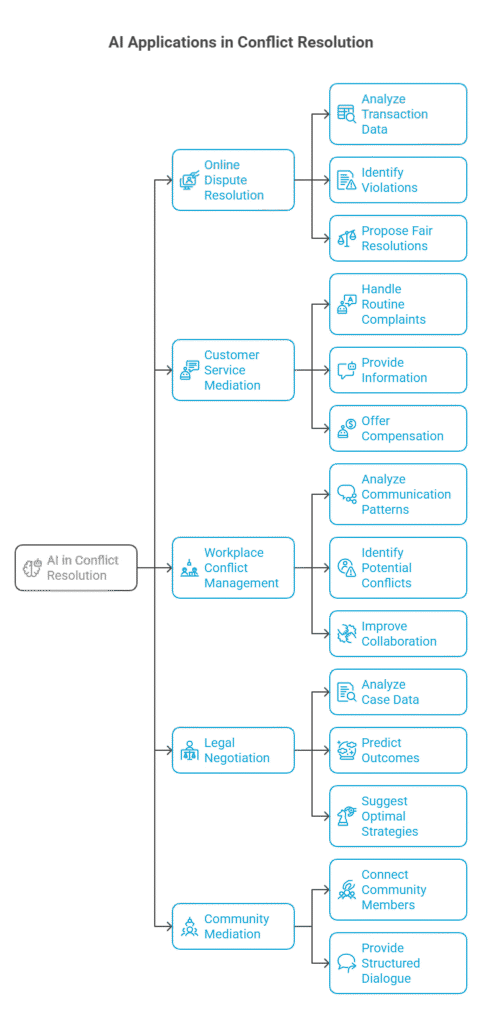
Online Dispute Resolution (ODR): E-commerce platforms and online marketplaces use AI-powered ODR systems to resolve disputes between buyers and sellers. These systems analyze transaction data, communication logs, and user feedback to identify violations of terms of service and propose fair resolutions.
Customer Service Mediation: Companies are deploying AI chatbots to mediate customer service disputes. These bots can handle routine complaints, provide information, and offer compensation or alternative solutions, freeing up human agents to focus on more complex cases.
Workplace Conflict Management: AI tools are used to analyze communication patterns within teams, identify potential conflicts, and provide recommendations for improving collaboration and resolving disagreements. These tools can also facilitate anonymous feedback and mediation sessions.
Legal Negotiation: AI agents are being developed to assist lawyers in legal negotiations. These agents can analyze case data, predict outcomes, and suggest optimal negotiation strategies, helping lawyers achieve better results for their clients.
Community Mediation: AI-powered platforms are used to facilitate community mediation sessions, connecting neighbors or community members in conflict and providing a structured environment for dialogue and resolution.
These examples illustrate the diverse applications of AI in conflict resolution, highlighting its ability to streamline processes, reduce costs, and improve outcomes across various domains.
How AI Agents Analyze and Interpret Conflicts
AI agents analyze and interpret conflicts by processing communication data, identifying key issues, and understanding the emotional and contextual nuances involved. The process typically begins with data collection, where the agent gathers text, voice, or other relevant inputs from the parties involved.
Using natural language processing (NLP), the AI agent breaks down the communication into understandable components such as sentences, phrases, and keywords. It then applies sentiment analysis to detect emotions like anger, frustration, or empathy, which helps in assessing the intensity and tone of the conflict.
Next, the agent identifies the main points of disagreement by extracting topics, claims, and demands from the dialogue. Machine learning models trained on historical conflict data help the agent recognize patterns and predict potential escalation points or areas where compromise is possible.
By combining linguistic analysis with contextual understanding, AI agents create a structured representation of the conflict, enabling them to suggest appropriate mediation strategies or responses tailored to the specific situation.
Example Python Code: Basic Sentiment Analysis with TextBlob
python
from textblob import TextBlob
def analyze_conflict_text(text):
blob = TextBlob(text)
sentiment = blob.sentiment
polarity = sentiment.polarity # Range from -1 (negative) to 1 (positive)
subjectivity = sentiment.subjectivity # Range from 0 (objective) to 1 (subjective)
return polarity, subjectivity
# Example usage
conflict_text = "I am really upset about the missed deadlines and lack of communication."
polarity, subjectivity = analyze_conflict_text(conflict_text)
print(f"Polarity: {polarity}, Subjectivity: {subjectivity}")This simple code snippet demonstrates how an AI agent might begin to interpret the emotional tone of conflict-related text, which is a foundational step in conflict analysis.
Techniques for Negotiation and Compromise Used by AI
AI agents employ a variety of negotiation and compromise techniques to facilitate conflict resolution effectively. These techniques are designed to mimic human negotiation strategies while leveraging computational power to analyze data and optimize outcomes.
One common approach is interest-based negotiation, where the AI identifies the underlying interests and needs of each party rather than focusing solely on their stated positions. By understanding what truly matters to each side, the agent can propose solutions that satisfy core concerns and create win-win scenarios.
Another technique is multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA), which helps the AI evaluate different options based on multiple factors such as cost, time, and satisfaction levels. This allows the agent to suggest compromises that balance competing priorities fairly.
AI agents also use game theory models to predict the behavior of parties and anticipate possible responses to various proposals. This strategic insight helps the agent craft offers that are more likely to be accepted and avoid deadlocks.
Iterative bargaining is another method, where the AI facilitates a series of proposals and counterproposals, gradually narrowing differences until an agreement is reached. Throughout this process, the agent monitors emotional cues and communication patterns to adjust its strategy dynamically.
Finally, AI agents may incorporate mediated communication techniques, such as reframing negative statements into neutral language or highlighting common goals, to reduce tension and foster cooperation.
By combining these techniques, AI agents can guide conflicting parties toward mutually acceptable agreements efficiently and impartially.
Ethical Considerations in AI-Driven Conflict Resolution
The use of AI in conflict resolution raises important ethical questions that must be carefully addressed to ensure fairness, transparency, and respect for all parties involved.
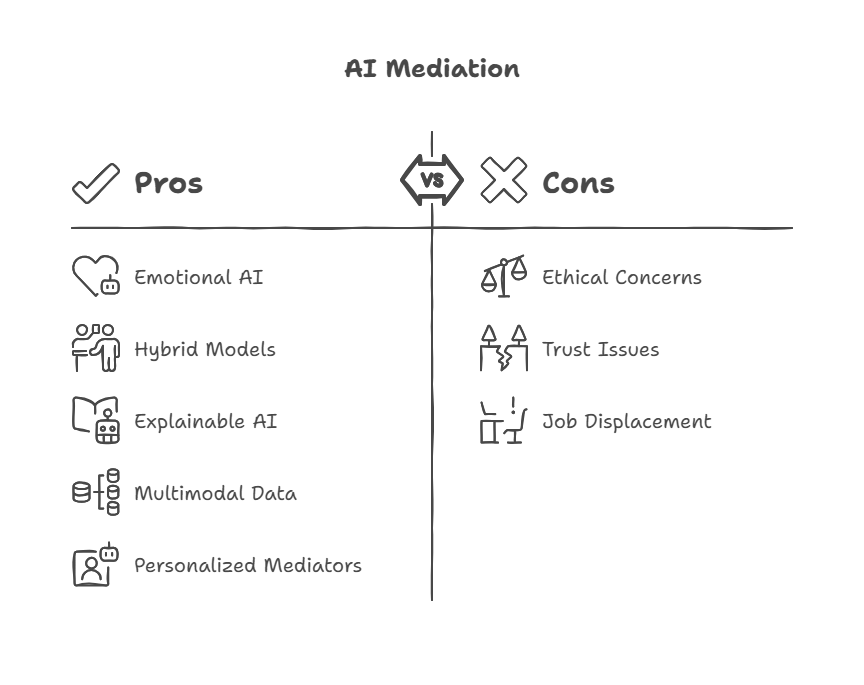
One major concern is bias and fairness. AI systems learn from historical data, which may contain biases reflecting social, cultural, or institutional prejudices. If not properly managed, these biases can lead to unfair treatment or reinforce existing inequalities in mediation outcomes. Ensuring diverse and representative training data, along with ongoing bias audits, is essential.
Transparency and explainability are also critical. Parties involved in a conflict have the right to understand how decisions or recommendations are made by AI agents. Black-box models that provide no insight into their reasoning can undermine trust and acceptance. Designing AI systems that offer clear explanations for their suggestions helps build confidence and accountability.
Privacy and confidentiality must be rigorously protected. Conflict resolution often involves sensitive personal or organizational information. AI agents need secure data handling practices and compliance with relevant regulations to safeguard participants’ privacy.
Another ethical aspect is autonomy and consent. Participants should have control over whether and how AI is used in their mediation process. They must be informed about the AI’s role and capabilities and have the option to opt out or seek human mediation if preferred.
Finally, there is the question of responsibility and liability. When AI agents make recommendations or decisions, it must be clear who is accountable for the outcomes—whether it is the developers, the deploying organization, or the users themselves.
Addressing these ethical considerations is vital to harness the benefits of AI in conflict resolution while maintaining trust, fairness, and respect for human dignity.
Challenges and Limitations of AI Mediators
AI mediators bring many advantages to conflict resolution, but they also face significant challenges and limitations that must be acknowledged.
Understanding Context and Nuance: Human conflicts often involve complex emotions, cultural backgrounds, and subtle social cues. AI systems, despite advances in natural language processing, can struggle to fully grasp these nuances. Misinterpretation of tone, sarcasm, or implicit meanings can lead to inappropriate or ineffective mediation suggestions.
Handling Ambiguity and Unstructured Data: Conflicts are rarely straightforward. Conversations may be fragmented, incomplete, or ambiguous. AI agents need sophisticated models to interpret such data accurately, but errors can still occur, affecting the quality of mediation.
Emotional Intelligence: Empathy and emotional support are crucial in conflict resolution. AI lacks genuine emotional understanding and may fail to provide the human warmth and reassurance that parties often need to feel heard and respected.
Bias and Fairness: As mentioned earlier, AI models trained on biased data can perpetuate unfairness. Detecting and mitigating bias remains a technical and ethical challenge.
Dependence on Quality Data: AI mediators require large amounts of high-quality, relevant data to learn effective mediation strategies. In many domains, such data may be scarce or difficult to obtain.
Legal and Ethical Constraints: AI recommendations may not always align with legal standards or ethical norms, especially in sensitive disputes. Human oversight is necessary to ensure compliance and appropriateness.
Example Python Code: Detecting Ambiguity in Text Using Simple Heuristics
One way AI might flag potentially ambiguous or unclear statements is by checking for vague words or phrases. Here’s a simple Python example that scans text for common ambiguous terms:
python
def detect_ambiguity(text):
ambiguous_terms = ['maybe', 'perhaps', 'somehow', 'possibly', 'unclear', 'vague', 'not sure']
found_terms = [term for term in ambiguous_terms if term in text.lower()]
if found_terms:
return True, found_terms
else:
return False, []
# Example usage
conflict_statement = "I'm not sure if the deadline can be met, maybe we need more time."
is_ambiguous, terms = detect_ambiguity(conflict_statement)
print(f"Ambiguity detected: {is_ambiguous}, Terms found: {terms}")This simple heuristic helps an AI mediator identify statements that may require further clarification or human intervention.
Case Studies: Successful Implementations of AI Mediation
AI mediation has been successfully implemented in various domains, demonstrating its potential to enhance conflict resolution processes by improving efficiency, objectivity, and accessibility.
One notable case is in online dispute resolution (ODR) platforms used by e-commerce marketplaces. AI agents help mediate conflicts between buyers and sellers by analyzing communication, identifying key issues, and suggesting fair settlements. For example, platforms like eBay and PayPal have integrated AI tools that reduce resolution time and increase user satisfaction by providing automated negotiation support and outcome recommendations.
In the workplace environment, some companies have adopted AI-driven tools to assist HR departments in resolving employee disputes. These AI agents analyze emails, chat logs, and feedback to detect early signs of conflict and propose mediation strategies. This proactive approach helps prevent escalation and fosters a healthier work culture.
Another successful implementation is in legal mediation support, where AI assists mediators by summarizing case facts, highlighting relevant precedents, and suggesting compromise options based on historical data. This support enables human mediators to make more informed decisions and manage caseloads more effectively.
In community conflict management, AI chatbots have been deployed to facilitate dialogue between disputing parties in a neutral, accessible manner. These chatbots guide users through structured conversations, helping them articulate concerns and explore solutions without the need for immediate human intervention.
These case studies illustrate how AI mediation can complement human expertise, making conflict resolution more scalable and data-driven while maintaining fairness and transparency.
Future Trends in AI Mediation and Conflict Resolution
The future of AI mediation and conflict resolution is poised for exciting advancements driven by improvements in artificial intelligence, natural language processing, and human-computer interaction.
One key trend is the development of more emotionally intelligent AI agents. Future systems will better recognize and respond to human emotions through advanced sentiment analysis, voice tone detection, and facial expression recognition, enabling more empathetic and context-aware mediation.
Hybrid human-AI mediation models are expected to become more prevalent. In these setups, AI agents handle routine or data-intensive tasks—such as information gathering, pattern recognition, and initial proposal generation—while human mediators focus on nuanced judgment, ethical considerations, and emotional support. This collaboration can enhance efficiency without sacrificing the human touch.
Advances in explainable AI (XAI) will improve transparency, allowing parties to understand how AI agents arrive at their recommendations. This will build trust and facilitate wider adoption of AI mediation tools.
The integration of multimodal data—combining text, audio, video, and biometric signals—will provide richer context for AI agents, improving their ability to interpret complex interactions and tailor mediation strategies accordingly.
Moreover, personalized AI mediators that adapt to individual communication styles, cultural backgrounds, and conflict histories will offer more customized and effective resolutions.
Finally, the expansion of AI mediation into new domains such as international diplomacy, environmental disputes, and large-scale social conflicts holds promise for addressing challenges that are currently difficult to manage through traditional means.
These trends suggest a future where AI mediation becomes an indispensable tool, augmenting human capabilities to resolve conflicts more fairly, efficiently, and empathetically.
AI: Your programming assistant